Faculty of
Engineering &
Computer Science
Research Collaboration
This research investigates innovation in Pakistan’s ICT sector, focusing on perceptions of senior leadership to understand the limitations in innovation practices. Through qualitative interviews, it was found that most organizations engage in product innovation characterized by partial replication, driven mainly by external factors. To address these limitations, an Innovation Readiness Framework (IRF) was developed. The IRF offers practical strategies for organizations to assess current innovation efforts, identify gaps, and foster original innovation. By addressing challenges such as limited resources and regulatory constraints, the IRF aims to enhance competitiveness, support sustainable growth, and contribute to broader societal and economic
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
- University of Madinah, Madinah, Saudi Arabia
This study integrates Internet of Things (IoT) technology and deep learning for early detection of cotton leaf and boll diseases, which significantly impact crop yield and the agriculture-based economy. While previous research focused only on leaf diseases, this work expands detection to include boll diseases using a customized dataset of 7289 images across eight classes. Deep learning models—VGG16, InceptionV3, and a tailored model—were evaluated, with the tailored model showing comparable accuracy. The proposed IoT-based perception system enhances real-time monitoring, enabling timely intervention and preventive measures, ultimately supporting improved cotton productivity and reducing economic losses due to pest-related damage.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Institute of Business Management, Karachi, Pakistan
- University of Madinah, Medina, Saudi Arabia
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science and Technology, Karachi
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
- University of Loralai, Loralai, Baluchistan, Pakistan
Vehicular Sensor Networks (VSNs) are transforming transportation through automated, sensor-driven communication among vehicles, infrastructure, and users. A key challenge is managing heterogeneous traffic generated by diverse sensors. This study compares two recent MAC protocols—FROG-MAC and urgMAC—for handling such traffic. FROG-MAC uses packet fragmentation to prioritize urgent data, while urgMAC employs cross-layer mechanisms for differentiated service. Performance evaluation reveals that FROG-MAC offers superior results in delay, energy efficiency, and packet delivery ratio. These findings highlight FROG-MAC’s effectiveness in ensuring reliable, efficient communication in VSNs, making it a promising candidate for real-time traffic management and intelligent transportation system applications.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology and Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa University, Karachi, Pakistan
- Islamic University of Madinah, Madinah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
The hybrid communication architecture for real-time human fertility monitoring, combining an intrabody nano-sensor network for detecting eggs in the female fallopian tube with a body area network (BAN) for transmitting data to healthcare professionals and patients. Preliminary simulations using a particle-based stochastic simulator revealed key factors affecting system performance, including information rates, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), detection delay, and environmental conditions like viscosity and temperature. The architecture achieves data rates of up to 300 Mbps with low latency, minimal energy consumption, and high throughput. This innovative system offers potential for timely, accurate fertility monitoring and personalized care.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology and Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa University, Karachi, Pakistan
- Islamic University of Madinah, Madinah, Saudi Arabia
- Walton Institute of Information and Communication Systems Science, South East Technological University, Waterford, Ireland
This study utilizes the free space approach and Nicholson-Ross-Weir Conversion to calculate the relative permittivity of FR4, a common dielectric material. Simulations were conducted using CST-2019 over a frequency range of 8.5 GHz to 11.5 GHz, and experimental measurements were performed with a Vector Network Analyzer in an anechoic chamber to minimize external interference. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the free space technique and Nicholson-Ross-Weir Conversion in accurately determining FR4’s dielectric properties. The findings, showing good agreement between simulated and measured results, contribute to electromagnetic characterization and offer valuable insights for PCB design and high-frequency electronic devices.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology and Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Federal Urdu University Arts and Science Technology,Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
- Millennium Institute of Technology and Entrepreneurship
- King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- Gachon University, Seongnam-si, South Korea
This study explores the role of cryptography in enhancing information security, particularly through the use of hash functions. Cryptography secures data by converting it into unreadable ciphertext, which can only be decrypted by the intended recipient using a secret key. The research presents a comparative analysis of two widely used cryptographic hash algorithms, focusing on three key aspects: collision vulnerabilities, performance, and security (file integrity). By evaluating these factors, the study aims to guide users in selecting the most suitable hash function for their specific security needs, especially in an era where data protection and secure communication are increasingly critical.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship (MiTE), Karachi, Pakistan
- Karachi Institute of Economics & Technology
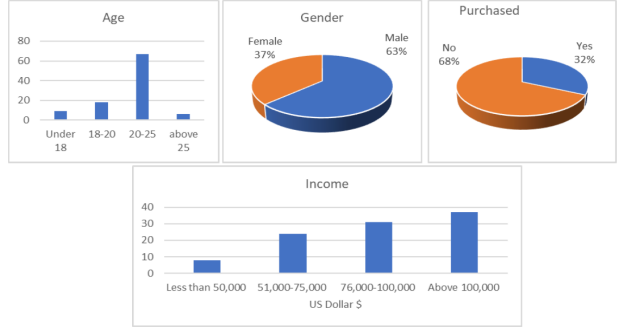
Social media advertising has significantly impacted brand recognition and consumer purchasing decisions. This study delved into the influence of social media advertisements on IoT device purchases among university students in Karachi, Pakistan. A survey of 100 students, selected through random sampling, was conducted. Data analysis revealed a positive correlation between income and IoT device ownership, while age and gender showed no significant influence. While social media ads and online reviews were identified as key factors influencing purchase decisions, the study also highlighted a gap in the IoT industry’s utilization of social media. The majority of respondents perceived IoT advertisements as uncreative and lacking in awareness creation. These findings underscore the need for IoT companies to enhance their social media marketing strategies to effectively reach and engage potential consumers.
Analysis of demographic factors (age, gender, income) and their correlation with consumer purchasing behavior for IoT devices.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
The proliferation of diverse applications has spurred the development of numerous protocols across various layers of the communication stack within the past two decades. MAC layer protocols have garnered significant attention due to their potential to optimize network performance. While numerous survey papers exist, a comprehensive guide to MAC protocol development remains scarce. This paper addresses this gap by offering a step-by-step tutorial, that exemplified the creation of ADP-MAC, a novel asynchronous MAC protocol. By introducing adaptive channel polling interval distributions, ADP-MAC outperforms existing protocols like SCP-MAC and T-AAD. This paper concludes by outlining key milestones in protocol development and providing recommendations for future research endeavors.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
- Institute of Business Administration, Karachi, Pakistan
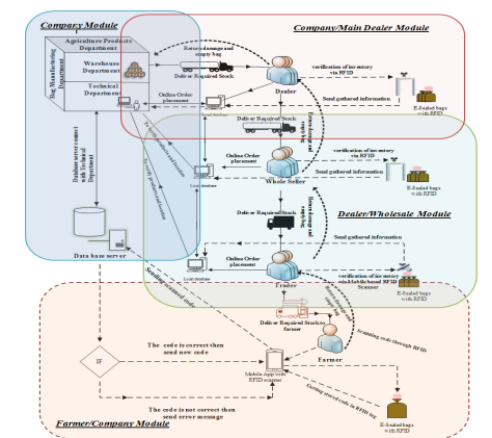
The agricultural supply chain, a dynamic and consumer-centric sector, has been a focal point of extensive research. Despite advancements, challenges persist in ensuring the quality and timely delivery of essential inputs like seeds, fertilizers, and agrochemicals. This research proposes a novel Smart E-seal-based supply chain model to address these issues. By integrating IoT and blockchain technologies, we aim to enhance transparency, traceability, and security. A rigorous evaluation using descriptive survey methods confirmed the model’s reliability and its potential to revolutionize agricultural supply chain management.
smart E-seal-based Agriculture Supply ChainModel
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
- Dawood University of Engineering & Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
Packet concatenation at the MAC layer is a critical technique for enhancing the efficiency of low-power IoT devices, particularly in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). Given the proliferation of packet concatenation schemes, this research compares the performance of ADP-MAC, a dynamic duty-cycling approach, with PiP, a concurrent transmission-based method. Through single-hop simulations on the Avrora emulator, ADP-MAC demonstrated a superior packet delivery ratio due to improved synchronization between nodes.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
The increasing adoption of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) in diverse applications, such as healthcare and surveillance, necessitates efficient handling of heterogeneous data traffic. This paper evaluates the performance of Priority-MAC and FROG-MAC, two MAC schemes designed for prioritizing data transmission. Priority-MAC employs differentiated TDMA slots, while FROG-MAC prioritizes urgent data by fragmenting low-priority traffic. Simulation results in a single-hop, 30-node environment demonstrate FROG-MAC’s superior performance in minimizing delay for urgent traffic compared to Priority-MAC. The study further investigates the impact of network and fragment size variations on urgent traffic delays within the FROG-MAC protocol.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan