Faculty of
Engineering &
Computer Science
Research Collaboration
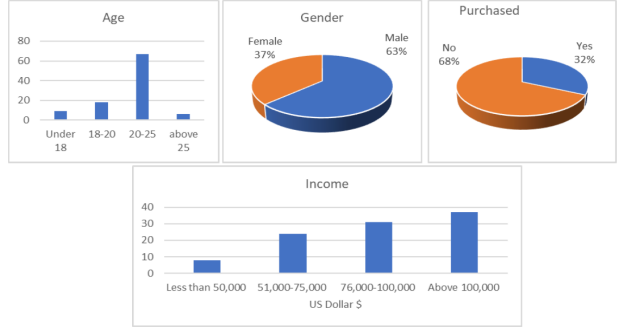
Social media advertising has significantly impacted brand recognition and consumer purchasing decisions. This study delved into the influence of social media advertisements on IoT device purchases among university students in Karachi, Pakistan. A survey of 100 students, selected through random sampling, was conducted. Data analysis revealed a positive correlation between income and IoT device ownership, while age and gender showed no significant influence. While social media ads and online reviews were identified as key factors influencing purchase decisions, the study also highlighted a gap in the IoT industry’s utilization of social media. The majority of respondents perceived IoT advertisements as uncreative and lacking in awareness creation. These findings underscore the need for IoT companies to enhance their social media marketing strategies to effectively reach and engage potential consumers.
Analysis of demographic factors (age, gender, income) and their correlation with consumer purchasing behavior for IoT devices.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
The proliferation of diverse applications has spurred the development of numerous protocols across various layers of the communication stack within the past two decades. MAC layer protocols have garnered significant attention due to their potential to optimize network performance. While numerous survey papers exist, a comprehensive guide to MAC protocol development remains scarce. This paper addresses this gap by offering a step-by-step tutorial, that exemplified the creation of ADP-MAC, a novel asynchronous MAC protocol. By introducing adaptive channel polling interval distributions, ADP-MAC outperforms existing protocols like SCP-MAC and T-AAD. This paper concludes by outlining key milestones in protocol development and providing recommendations for future research endeavors.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
- Institute of Business Administration, Karachi, Pakistan
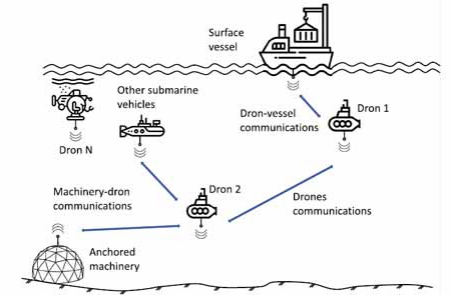
The imperative need for mobile sensor nodes in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs) has been evident for decades, driven by applications in underwater warfare, autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) exploration, and remote-operated vehicle (ROV) operations. While the development of protocols for ad hoc mobile UWSNs (AMUWSNs) is challenging due to the dynamic nature of the underwater environment and the inherent limitations of acoustic communication, there remains a dearth of suitable solutions. This paper introduces the Self-Organized Ad Hoc Mobile (SOAM) routing protocol for AMUWSNs. SOAM is a reactive, cluster-based approach that leverages Received Signal Strength (RSS) for distance estimation. By employing a beacon-based mechanism, the protocol establishes forwarding paths between cluster heads and a gateway, enabling efficient communication among ordinary sensor nodes.
Self-Organized Ad Hoc Mobile (SOAM) UWSNs: A novel routing protocol for dynamic underwater environments.
Contributors
- University of Malaga, Málaga, Spain
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Sindh Madressatul Islam University, Karachi, Pakistan
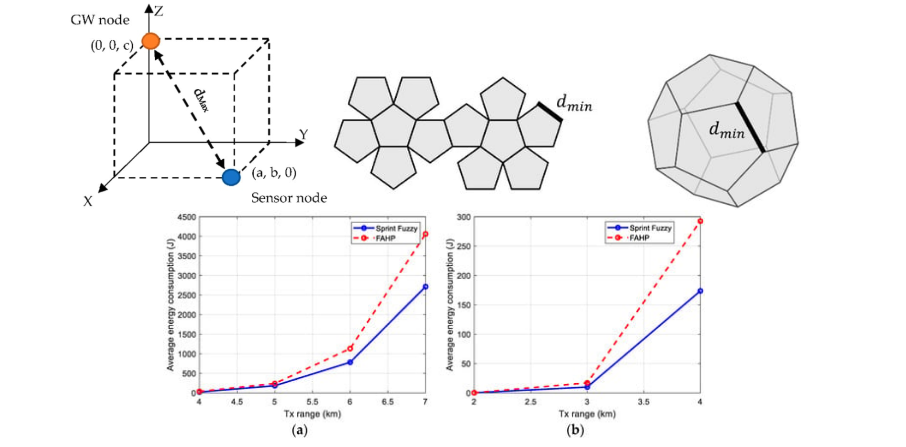
Underwater Sensor Networks (UWSNs) hold immense potential for monitoring aquatic environments and detecting geological events. However, the unique challenges posed by underwater conditions, such as limited bandwidth, significant latency, and dynamic topologies, necessitate innovative solutions. This paper introduces a novel energy-efficient routing protocol that adapts to the dynamic nature of UWSNs. By employing the Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process (FAHP) under Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM), our protocol intelligently selects optimal routes based on factors like hop count, distance to the sink, and node connectivity. Through rigorous evaluation, the proposed protocol demonstrated comparable performance to existing fuzzy-based routing schemes like SPRINT.
Analysis of maximum distance in a 3D box, dodecahedron geometry, collision frequency based on node density, and simulation results.
Contributors
- University of Malaga, Málaga, Spain
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Dawood University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
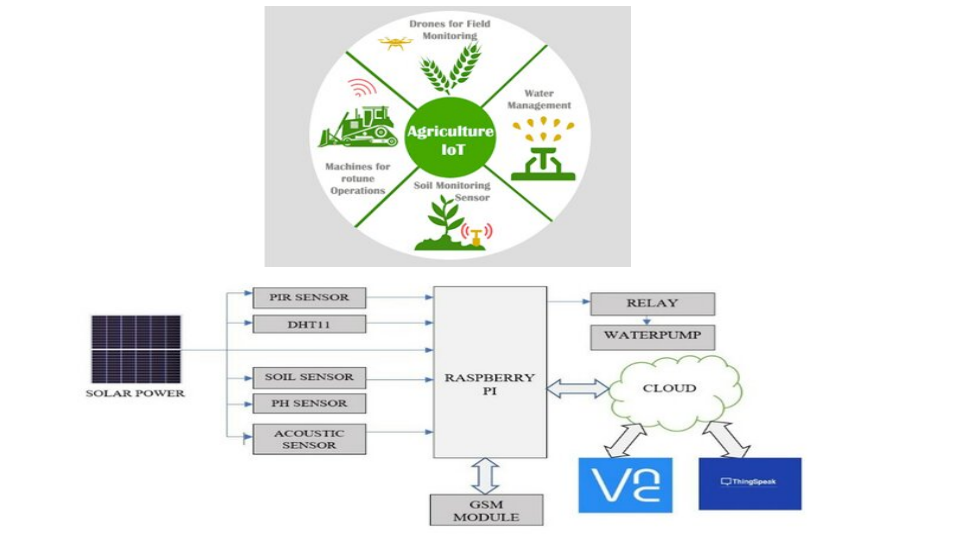
The IoT revolutionizes agriculture by addressing challenges like pest infestation, weather unpredictability, inefficient irrigation, and remote farm management. This research proposes an IoT-based solution to optimize crop yield and quality. By integrating sensors for pest monitoring, environmental conditions, and irrigation control, coupled with GSM and VNC for remote management, our system offers a cost-effective and efficient approach. Real-time data is collected and analyzed, enabling informed decision-making. This architecture holds the potential to significantly enhance agricultural practices, particularly in regions like Pakistan where traditional methods persist.
Proposed framework and key IoT application areas within the research.
Contributors
- Macquarie University, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Mehran University, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan
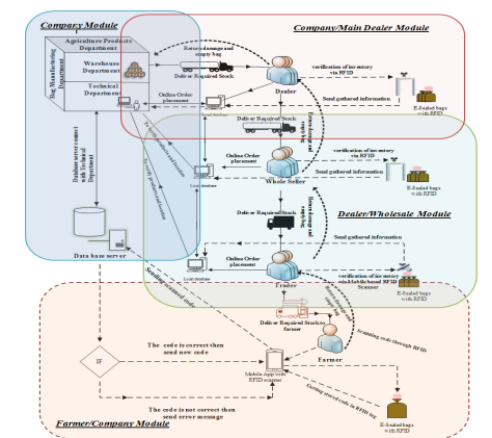
The agricultural supply chain, a dynamic and consumer-centric sector, has been a focal point of extensive research. Despite advancements, challenges persist in ensuring the quality and timely delivery of essential inputs like seeds, fertilizers, and agrochemicals. This research proposes a novel Smart E-seal-based supply chain model to address these issues. By integrating IoT and blockchain technologies, we aim to enhance transparency, traceability, and security. A rigorous evaluation using descriptive survey methods confirmed the model’s reliability and its potential to revolutionize agricultural supply chain management.
smart E-seal-based Agriculture Supply ChainModel
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
- Dawood University of Engineering & Technology, Karachi, Pakistan
Packet concatenation at the MAC layer is a critical technique for enhancing the efficiency of low-power IoT devices, particularly in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). Given the proliferation of packet concatenation schemes, this research compares the performance of ADP-MAC, a dynamic duty-cycling approach, with PiP, a concurrent transmission-based method. Through single-hop simulations on the Avrora emulator, ADP-MAC demonstrated a superior packet delivery ratio due to improved synchronization between nodes.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan
The increasing adoption of Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) in diverse applications, such as healthcare and surveillance, necessitates efficient handling of heterogeneous data traffic. This paper evaluates the performance of Priority-MAC and FROG-MAC, two MAC schemes designed for prioritizing data transmission. Priority-MAC employs differentiated TDMA slots, while FROG-MAC prioritizes urgent data by fragmenting low-priority traffic. Simulation results in a single-hop, 30-node environment demonstrate FROG-MAC’s superior performance in minimizing delay for urgent traffic compared to Priority-MAC. The study further investigates the impact of network and fragment size variations on urgent traffic delays within the FROG-MAC protocol.
Contributors
- Millennium Institute of Technology & Entrepreneurship, Karachi, Pakistan
- DHA Suffa, Karachi, Pakistan